alcohol lucas test|Lucas Test: Definition, Examples, Test for Alcohols, Mechanism : Tagatay Lucas test is performed to distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols and which alcohol gives the fastest alkyl halide. Lucas test is based on the difference in . Our Craftool® Pro Embossing Tools are great for fast and easy borders! These borders measure 3/8" and are for use on cased leather. Designed to fit Craftool® Embossing Hand Tool (sold separately). Specifications Dimensions: 0.63 in. x 0.59 in. (1.6 cm x 1.5 cm) Embossing Width: 0.39 in. (1 cm)
PH0 · Lucas' reagent
PH1 · Lucas Test: Definition, Examples, Test for Alcohols, Mechanism
PH2 · Lucas Test
PH3 · Lucas Reagent Formula, Test, Preparation, Mechanism,
PH4 · Identifying Alcohols: Ferric Chloride Test, Jones Test, and Lucas
PH5 · Chemical Tests for Alcohols: Lucas Test & Oxidation
PH6 · 6.4D: Individual Tests
Professional Regulation Commission
alcohol lucas test*******Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Alcohols are classified based on their reactivity with the Lucas reagent. The reaction that occurs in the Lucas test can be seen as a nucleophilic substitution reaction. In this reaction, the Chloride in the zinc-chloride bond is replaced with a hydroxyl group originating . Tingnan ang higit pa
As discussed earlier, the test can be used to differentiate the reaction speed of the alcohol with the given Lucas reagent. This is done by measuring the . Tingnan ang higit paThe mechanism followed in this reaction is an SN1 nucleophilic substitution. It can be broken down into the following two steps. Tingnan ang higit pa Lucas test is performed to distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols and which alcohol gives the fastest alkyl halide. Lucas test is based on the difference in .
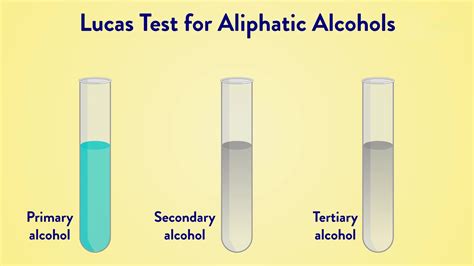
The Lucas reagent (concentrated \(\ce{HCl}\) and \(\ce{ZnCl_2}\)) is a test for some alcohols. Alcohols can react through an \(S_\text{N}1\) mechanism to produce alkyl .Lucas Test: Definition, Examples, Test for Alcohols, MechanismThe Lucas reagent (concentrated \(\ce{HCl}\) and \(\ce{ZnCl_2}\)) is a test for some alcohols. Alcohols can react through an \(S_\text{N}1\) mechanism to produce alkyl . The Lucas test was given by Howard Lucas in the year 1930 for the detection of alcohols using the solution of zinc chloride in concentrated hydrochloric .A simple reaction is given below: ZnCl 2. ROH + HCl—>RCl + H 2 O. The tertiary alcohol undergoes the most stable reaction and the primary alcohol undergoes the least stable .Lucas Test. The Lucas test utilizes zinc (II) chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid as a reagent. In the presence of an alcohol, the Lucas reagent will halogenate the alcohol, .
The Lucas test in alcohols is a test to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols. It is based on the difference in reactivity of the three classes of alcohols .In this lab, you will identify an unknown alcohol using the ferric chloride test, the Jones test, and the Lucas test. You'll test known alcohols alongside the unknown alcohol as .The Lucas Test uses the reaction rate to distinguish between the three types of aliphatic alcohols. Tertiary alcohols react immediately, forming a secondary phase in the reaction .
Science Ready. 9.37K subscribers. Subscribed. 117. 11K views 2 years ago HSC Chemistry Module 8 – Applying Chemical Ideas. This video explores the Lucas test and oxidation tests using.

Therefore, the Jones test can help differentiate primary and secondary alcohols from tertiary alcohols. Lucas Test. The Lucas test utilizes zinc(II) chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid as a reagent. In the presence of an alcohol, the Lucas reagent will halogenate the alcohol, making an insoluble product in aqueous solutions.Reaction of alcohols with hydrogen halides (HX) In Lucas test, alcohols react at different rates to form a turbid solution. A stable carbocation will produce turbidity much faster than an unstable carbocation. A student treats the given 3 different alcohols with Lucas reagent and gets the following results. Lucas test for the distinction of alcohols: The Lucas reagent is an equimolar mixture of ZnCl 2 and HCl. In this method, few drops of Lucas reagent is added to the given sample of alcohol in a test .
Figure 5-8. The Lucas test is a visual method to differentiate primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols by their varying ease of conversion to chlorides. A separate layer of alkyl chloride is observed in a positive test. Reaction of t-butyl alcohol with HCl to produce water insoluble t-butyl chloride. Heating an alcohol with H 2 S0 4 results .
These authors performed the Lucas test on a number of alcohols and discuss the problems associated with the Lucas test's detection of secondary alcohols. KEYWORDS (Audience): Second-Year Undergraduate
Lucas Test For Alcohols. The Lucas test differentiates between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols by using Lucas’ reagent: concentrated HCl, ZnCl 2 (catalyst). HCl causes substitution reaction with the hydroxyl functional group, resulting in the production of a halogenated hydrocarbon. The halogenated product has lower solubility in water.View Solution. Lucas test is used to differentiate and categorize primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols using a solution of anhydrous zinc chloride in concentrated hydrochloric acid. This solution is commonly referred to as “Lucas Reagent”. 2-Methyl-2-butonol can be differentiated from 3-methyl-2-butanol using Lucas reagent because:
In the laboratory, one can test for the presence of alcohols with Lucas reagent (a mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride). Lucas reagent converts alcohols to alkyl chlorides: tertiary alcohols give an immediate reaction, indicated when the alcohol solution turns cloudy; secondary alcohols usually show evidence of reacting .
Lucas Test for Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alcohols. 1-butanol, 2-butanol, and 2-methyl-2-propanol are treated with a solution of ZnCl 2 in concentrated aqueous HCl. Three test tubes contain a solution of zinc chloride (ZnCl 2) in concentrated aqueous hydrochloric acid (HCl). The primary alcohol 1-butanol, the secondary alcohol 2-butanol .Lucas-Probe. Die Lucas-Probe (auch Lucas-Test) ist eine Nachweisreaktion in der organischen Chemie zur Unterscheidung von primären, sekundären und tertiären Alkoholen. Dabei reagieren Alkohole abhängig von der Stellung der Hydroxygruppe im Molekül des Alkohols unter nucleophiler Substitution unterschiedlich schnell oder gar nicht. This video explores the Lucas test and oxidation tests using acidified dichromate and permanganate solutions to distinguish between primary, secondary and te.The Lucas test is used to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols, as well as to determine which alcohol produces the fastest alkyl halide. Using the Lucas test, you can determine the difference in reactivity between alcohols and hydrogen halide. The rates at which primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols react with .
Distinction Between Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Alcohols: Lucas Test: The mixture of zinc chloride and concentrated hydrochloric acid is called Lucas reagent. It reacts with primary, secondary and tertiary .
alcohol lucas test Lucas Test: Definition, Examples, Test for Alcohols, MechanismFor the Lucas test, the test tube containing t-butyl alcohol turn cloudy instantly from colourless solution. This is because t-butyl alcohol is a tertiary alcohol. The tertiary alcohol react instantly with lucas reagent due to formation of the stable tertiary carbocation. For benzyl alcohol, the observation is colourless solution turn cloudy .
Therefore, the Jones test can help differentiate primary and secondary alcohols from tertiary alcohols. Lucas Test. The Lucas test utilizes zinc(II) chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid as a reagent. In the presence of an alcohol, the Lucas reagent will halogenate the alcohol, making an insoluble product in aqueous solutions.In this lab, you will identify an unknown alcohol using the ferric chloride test, the Jones test, and the Lucas test. You'll test known alcohols alongside the unknown alcohol as examples of positive and negative results for each test. The four known alcohols are 1-butanol, a primary alcohol, 2-butanol, a secondary alcohol, 2-methyl-2-propanol .盧卡斯 報導以來 .
Using alcohol reactivity to distinguish between classifications. The presence of an alcohol can be determined with test reagents that react with the -OH group. The initial test to identify alcohols is to take the neutral liquid, free of water and add solid phosphorus (V) chloride. A a burst of acidic steamy hydrogen chloride fumes indicate the .
Royal888 . r88
alcohol lucas test|Lucas Test: Definition, Examples, Test for Alcohols, Mechanism